gBay
Bayesian Networks with geo-data
Bayesian networks (BNs) are a powerful tool to represent complex socio-ecological systems, as they can take into account both qualitative and quantitative data, while the associated uncertainties are explicitly shown and propagated through the network. Furthermore, relationships between variables in the BN are represented graphically, creating a transparent model structure that can facilitate communication with stakeholders. Because of these advantages, BNs are increasingly used to model land use change and ecosystem services.
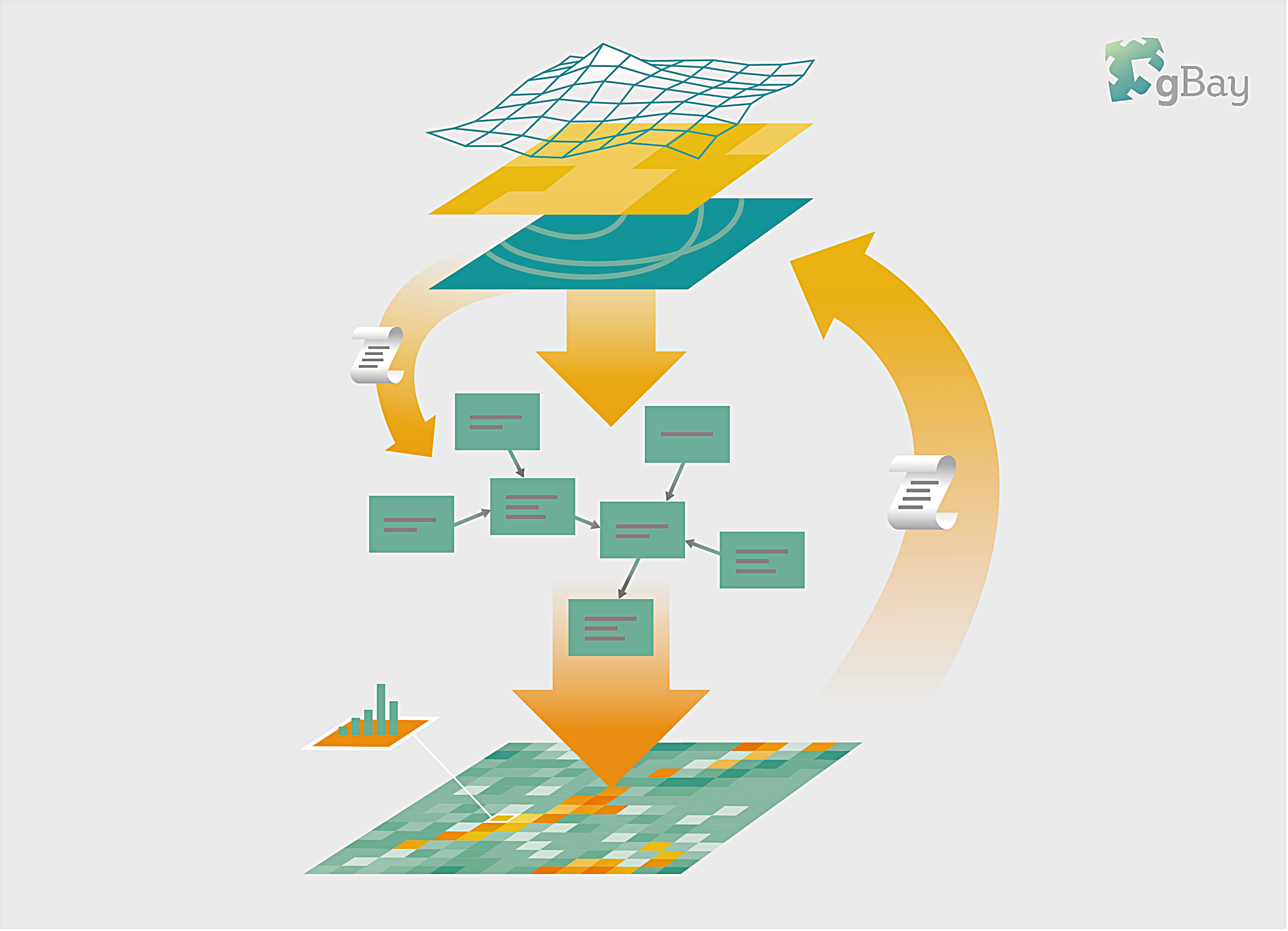
gBay is a toolbox that links BNs to spatial (raster or vector) data. For each pixel (or polygon), the values in the input data are used as evidence in the network, and inference is performed to obtain the posterior probability distribution of the target nodes. Then, the posterior distributions of the target nodes are written into a new spatial file.
gBay supports dynamic BNs – running the network over multiple time steps, where the output of one time step is an input to the next, which can be used to model feedback loops. Advanced users can also modify spatial data directly in gBay, which allows them to take into account spatial interactions such as neighbourhood effects.
Contents:
- Examples of BNs for ecosystem services
gBay was developed at ETH-PLUS and is partially supported by the ECOPOTENTIAL project (funded by the European Union's Horizon 2020 research and innovation programme under grant agreement No 641762).
When using gBay, please refer to the following publication:
Stritih, A., Rabe, S. E., Robaina, O., Grêt-Regamey, A. & Celio, E. 2020. An online platform for spatial and iterative modelling with Bayesian Networks. Environmental Modelling and Software, 127. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envsoft.2020.104658
Contact: Ben Black bblack@ethz.ch