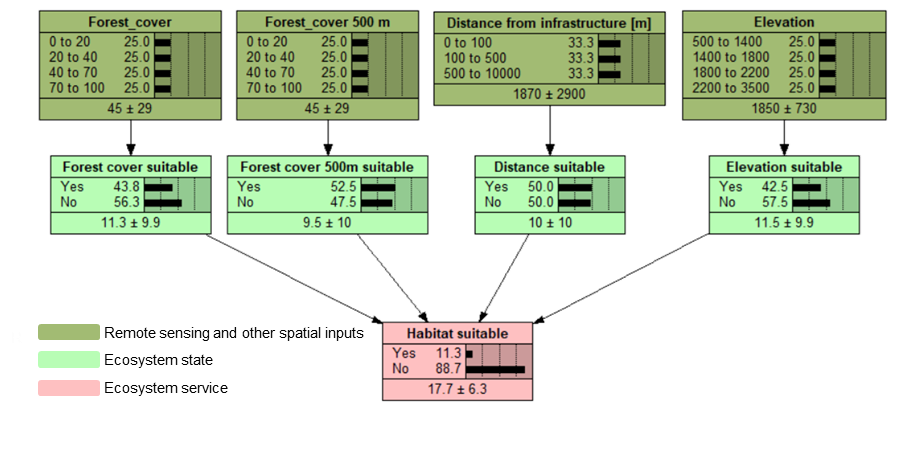
Habitat suitability
The model describes the habitat suitability for a grouse species in the Alps. The grouse mainly live in montane, not-too-dense conifer forests (with 40-70% tree cover), where there is enough light for understory vegetation such as blueberries. Large forest areas are more suitable than small patches, so the model takes into account nearby pixels within a 500 m distance (calculated within gBay using a script to Calculate mean value in neighbouring cells). Since the birds are sensitive to human disturbance, the distance from infrastructure is also an important factor.
For each continuous factor, we first define the thresholds to discretize the nodes. Then, we create additional nodes describing the suitability of each individual factor. Since all the factors need to be suitable in order to have a suitable habitat for grouse, the conditional probability of “habitat suitable” is defined as a Noisy-AND distribution of all its parents. In Netica, we write this using an equation:
p (Habitat | Forest_cover_suit, Forest_cover_500suit, Distance_suit, Elevation_suit) = NoisyAndDist(Habitat, pinh, Forest_cover_suit, p1, Forest_cover_500suit, p2, Distance_suit, p3, Elevation_suit, p4)
Where pinh is the probability that the habitat is not suitable even if all the individual factors are suitable, and p1-4 are the probabilities that each factor will be required for the habitat to be suitable.
Download this network and spatial data to run this network with gBay.